User Tools
Sidebar
This is an old revision of the document!
Table of Contents
How To Use The Uart
About this Article
- Author: allen — allen@cubietech.com — 2014/03/26 16:50
- Copyrights: CC Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported
- Contributors: Cubieboard Community : …
Abstract
Here is the guide to teach that how to enable the uart port on cubiboard and how to test the uart port is available .
Cubieboard pin
Cubietruck http://docs.cubieboard.org/a20-cubietruck_gpio_pin
Cubieboard 1 2 http://docs.cubieboard.org/cubieboard1_and_cubieboard2_gpio_pin
Fex Guide http://linux-sunxi.org/Fex_Guide
Open the port
#mount /dev/nanda /mnt #cd /mnt #bin2fex script.bin script.fex #vi script.fex
Modify the script.fex to open the uart3 ,uart4 as below :
[uart_para3] uart_used = 1 uart_port = 3 uart_type = 4 uart_tx = port:PG06<4><1><default><default> uart_rx = port:PG07<4><1><default><default> uart_rts = port:PG08<4><1><default><default> uart_cts = port:PG09<4><1><default><default> [uart_para4] uart_used = 1 uart_port = 4 uart_type = 2 uart_tx = port:PG10<4><1><default><default> uart_rx = port:PG11<4><1><default><default>
Save the modification.
#fex2bin script.fex script.bin #reboot
After the reboot ,the uart3 and uart4 are available.
Test the uart
Write a internal loopback program to test the uart .
#vi uart_test.c
Edit the program
/********************************************************************
**************************uart_test*********************************
********************************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <string.h>
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE -1
int speed_arr[] = {B115200, B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300,
B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300, };
int name_arr[] = {115200, 38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300,
38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300, };
void set_speed(int fd, int speed)
{
int i;
int status;
struct termios Opt;
tcgetattr(fd,&Opt);
for (i= 0;i<sizeof(speed_arr)/sizeof(int);i++)
{
if(speed == name_arr[i])
{
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH);
cfsetispeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]);
cfsetospeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]);
status = tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &Opt);
if(status != 0)
perror("tcsetattr fd1");
return;
}
tcflush(fd,TCIOFLUSH);
}
}
int set_Parity(int fd,int databits,int stopbits,int parity)
{
struct termios options;
if( tcgetattr( fd,&options)!= 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return(FALSE);
}
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch(databits)
{
case 7:
options.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
options.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported data size\n");
return (FALSE);
}
switch(parity)
{
case 'n':
case 'N':
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; /* Clear parity enable */
options.c_iflag &= ~INPCK; /* Enable parity checking */
options.c_iflag &= ~(ICRNL|IGNCR);
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON );
break;
case 'o':
case 'O':
options.c_cflag |= (PARODD | PARENB);
options.c_iflag |= INPCK; /* Disnable parity checking */
break;
case 'e':
case 'E':
options.c_cflag |= PARENB; /* Enable parity */
options.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
options.c_iflag |= INPCK; /* Disnable parity checking */
break;
case 'S':
case 's': /*as no parity*/
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported parity\n");
return (FALSE);
}
switch(stopbits)
{
case 1:
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
case 2:
options.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported stop bits\n");
return (FALSE);
}
/* Set input parity option */
if(parity != 'n')
options.c_iflag |= INPCK;
options.c_cc[VTIME] = 150; // 15 seconds
options.c_cc[VMIN] = 0;
tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH); /* Update the options and do it NOW */
if(tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&options) != 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 3");
return (FALSE);
}
return (TRUE);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
int nread;
int nwrite;
int n=0;
int i=0;
char buffer[15];
char devname_head[10] = "/dev/";
char dev_name[20];
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("Please input './test_uart ttySx'\n");
exit(1);
}
else
{
strcpy(dev_name, devname_head);
strcat(dev_name, argv[1]);
}
fd = open(dev_name, O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0)
{
perror("error to open /dev/ttySx\n");
exit(1);
}
if (fd > 0)
{
set_speed(fd,115200);
}
else
{
printf("Can't Open Serial Port!\n");
exit(0);
}
if (set_Parity(fd,8,1,'N') == FALSE)
{
printf("Set Parity Error\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("\nWelcome to uart_test\n\n");
memset(buffer,0,sizeof(buffer));
char test[15] = "hello world";
nwrite = write(fd,test,strlen(test));
if(nwrite < 0)
{
printf("write error\n");
}
printf("Send test data------>%s\n",test);
while(1)
{
nread = read(fd,&buffer[n],1);
if(nread < 0)
{
printf("read error\n");
}
printf("read char is -> %c \n",buffer[n]);
if (strlen(buffer) == strlen(test))
{
printf("Read Test Data finished,Read Test Data is------->%s\n",buffer);
memset(buffer,0,sizeof(buffer));
printf("Send test data again------>%s\n",test);
write(fd,test,strlen(test));
n=0;
sleep(1);
continue;
}
n++;
}
}
Install software build the compiled enviroment .
#apt-get install gcc build-essential #gcc uart_test.c -o uart_test
To test uart3(or uart4) should make sure the PG06 and PG07 (or PG10 and PG11)internal loopback,use Dupont Line connect them .
If you only open the uart0 4, uart4 is mapping the device ttyS1.
While open the uart0 3 4, uart3 is mapping the device ttyS1. uart4 is mapping the device ttyS2.
#./uart_test ttyS1 // or ttyS2
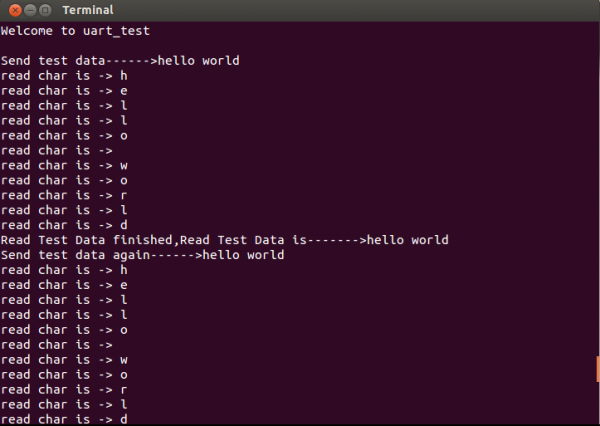
The termial will prinf as below,it prove the uart3 is working .